Lesson 28: Using React via Reagent
We have seen that React is a good platform for writing ClojureScript applications, but we have not yet written any code. While it is entirely possible to use the React API directly, we are going to be using Reagent, which provides a very simple API that lets us concern ourselves with writing components rather than fiddling with React lifecycle and complex state management. Reagent components use the same hiccup-style DOM representation that we used back in Lesson 20 when we wrote the Contact Book application. Reagent also comes with built-in state management, which uses atoms to keep track of data. Our process for writing Reagent applications will be similar to the process we used in Lesson 20, except we can rely on Reagent and React to automatically and efficiently re-render when our state is updated.
In this lesson:
- Defining a data model using (reactive) atoms
- Querying and updating application state
- Creating different types of Reagent components
Reactive Data
In the last lesson, we mentioned that React follows a reactive programming model. This is true of Reagent’s state management as well. Reagent provides a specialized atom called a reactive atom that can keep track of when it is dereferenced (i.e, when @atom or (deref atom) is called). If it is dereferenced inside a Reagent component, it will signal to Reagent to re-render the component. To see how values can reactively flow through a system, we can create the spreadsheet cell example from the last chapter using some of Reagent’s reactive primitives. First, we’ll initialize a new Figwheel project:
$ clj -X:new :template figwheel-main :name learn-cljs/reagent-test :args '["+deps"]'
$ cd reagent-test
Next, we need to add reagent as a dependency in deps.edn:
:deps {;; Other deps...
reagent/reagent {:mvn/version "1.0.0"}}
Now we can replace the body of the default HTML file that Figwheel generates with our HTML that contains a few inputs cells for the world’s simplest spreadsheet:
<h1>Reactive Cells</h1>
<div>
<label for="cell-a">A: </label>
<input id="cell-a" type="number" value="0" />
</div>
<div>
<label for="cell-b">B: </label>
<input id="cell-b" type="number" value="0" />
</div>
<div>
<label for="cell-c">C: </label>
<input id="cell-c" readonly type="number" />
</div>
resources/public/index.html
Now we are ready to hook this page up to Reagent for state management. In the learn-cljs.reagent-test namespace, we will create 2 reactive atoms to represent the A and B cells and a reaction that represents the C cell, whose value will be updated whenever one of the other cells changes.
(ns learn-cljs.reagent-test
(:require [reagent.core :as r] ;; <1>
[reagent.ratom :as ratom] ;; <2>
[goog.dom :as gdom]
[goog.events :as gevents]))
(def a-cell (r/atom 0)) ;; <3>
(def b-cell (r/atom 0))
(def c-cell
(ratom/make-reaction ;; <4>
#(+ @a-cell @b-cell)))
(def a (gdom/getElement "cell-a"))
(def b (gdom/getElement "cell-b"))
(def c (gdom/getElement "cell-c"))
(defn update-cell [cell]
(fn [e]
(let [num (js/parseInt (.. e -target -value))]
(reset! cell num))))
(gevents/listen a "change" (update-cell a-cell)) ;; <5>
(gevents/listen b "change" (update-cell b-cell))
(ratom/run! ;; <6>
(set! (.-value c) @c-cell))
src/reagent_test/core.cljs
reagent.coreprovides the reactive version ofatomreagent.ratomprovides several reactive programming utilitiesa-cellandb-cellare reactive atomsc-cellis a reaction, which acts like an atom whose value is derived from other reactive atoms- Update the corresponding cell when the input for A or B changes
- Use
ratom/run!to update the C input wheneverc-cellchanges
If we run this example, we will see a page with 3 inputs labeled A, B, and C. A and B are normal number inputs, and C is a read-only input that displays the result of adding A and B together. We create reactive atoms for the A and B cells using reagent.core/atom, which act like regular atoms that can propagate changes to other computations the rely upon them. We then create the C cell as a reaction to the other 2 cells. Since we dereference the a-cell and b-cell atoms within this reaction, Reagent creates a dependency relationship between Both A -> C and B -> C such that the value of C is updated reactively upon any change to A or B. As a reaction, C itself acts as a read-only reactive atom, and it could be used inside another reaction, which could be used inside another reaction, etc. A whole system of reactive atoms and reactions form a directed acyclic graph (DAG) such that any “upstream” changes automatically propagate “downstream” as far as they are able.
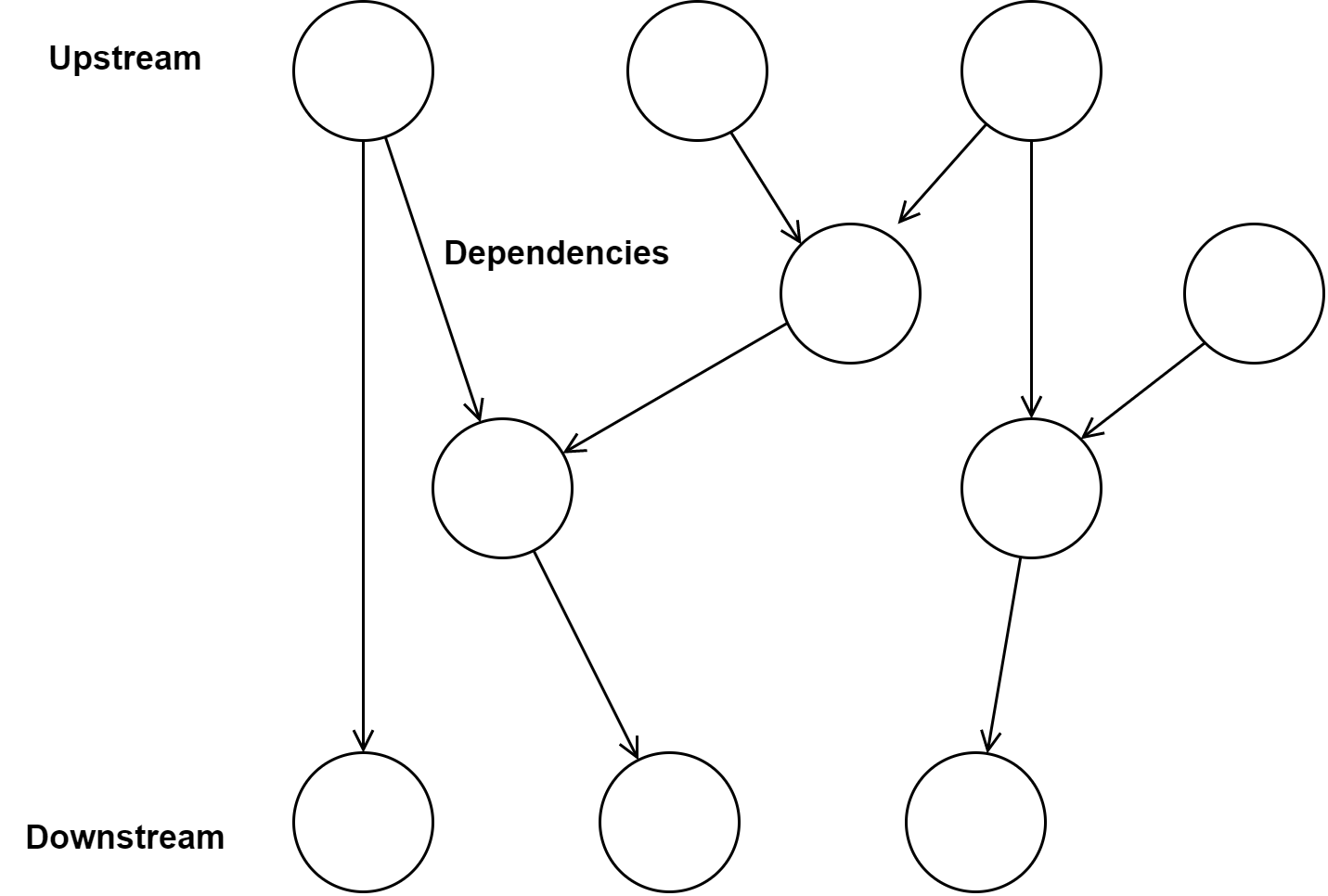
A Directed Acyclic Graph
We will come back to the concept of reactive data later when we see how to apply it to creating data-driven components, but first, we’ll look at components themselves.
Building Components
Reagent components are a very simple, declarative way to build up a virtual DOM structure to hand to React for rendering. A component is simply a function that returns a hiccup-like data structure. In the interest of sticking to tradition, we’ll create a component that prints the text “Hello World” inside a p tag:
(defn hello []
[:p "Hello World"])
That’s it. That is our first Reagent component that defines a single element. An element represents a tag where the first element is a keyword version of the tag name, an optional second element can contain a map of attributes, and the remaining items are children, which can be text, other elements, or other Reagent components.
We have a component, so now what? We need some way to render this component to the actual DOM. We can do this with the reagent-dom.render function, which takes just 2 arguments: a Reagent component and a DOM node to render it to. First, let’s create a new Reagent project that we will use for the rest of this lesson. This will be a very simple app that allows us to enter how many minutes we exercised on a given day, and it will chart our exercise over time.
$ clj -X:new :template figwheel-main :name learn-cljs/exercise-tracker :args '["+deps"]'
$ cd exercise-tracker
Next, we’ll add Reagent as a dependency just like we did in the previous section (not shown). Now, let’s update the learn-cljs.exercise-tracker namespace with the hello component, and we will also render this component to the DOM.
(ns learn-cljs.exercise-tracker
(:require [reagent.dom :as rdom]
[goog.dom :as gdom]))
(defn hello []
[:p "Hello World"])
(rdom/render
hello ;; <1>
(gdom/getElement "app")) ;; <2>
src/exercise_tracker/core.cljs
- Component to render
- DOM node to mount our component into
If we run clj -A:fig:build, we can see the Hello World printed to the screen:
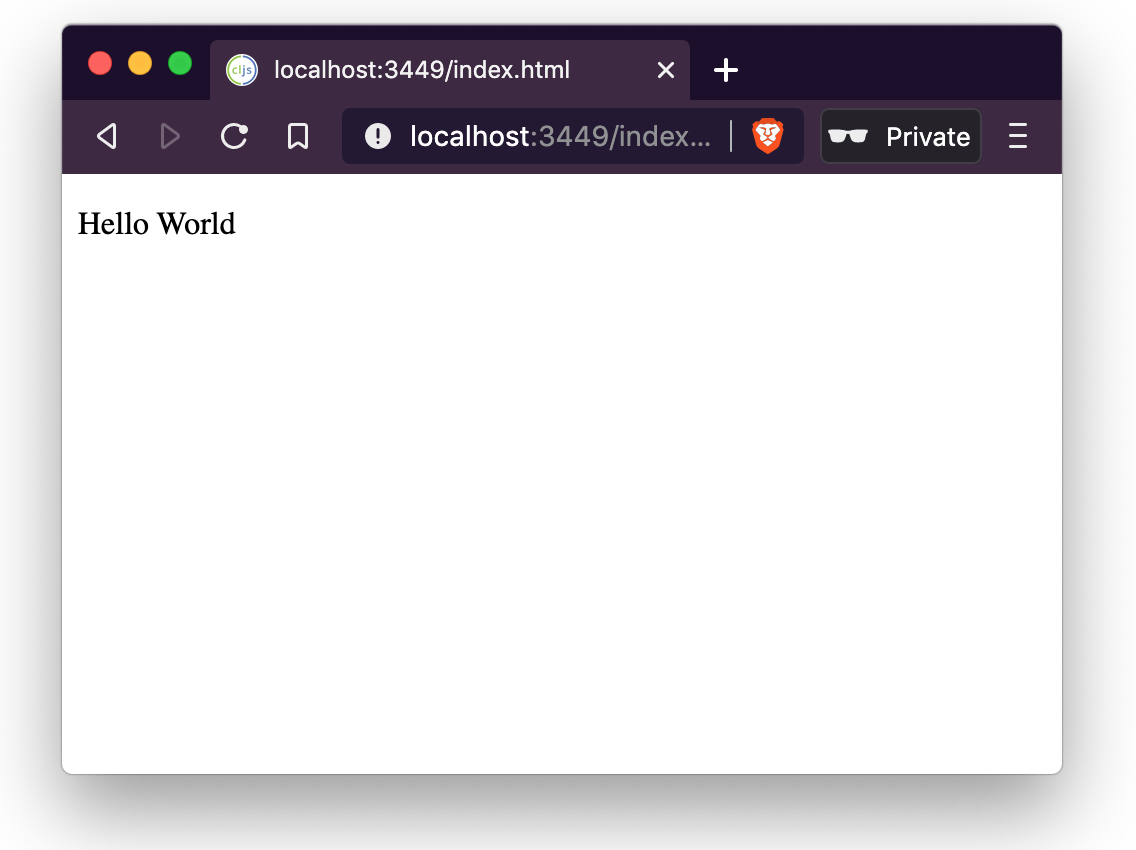
Reagent Hello World
While this is far from interesting in what it does, something is interesting about the structure: we have a single entry point (the call to rdom/render) that performs a side effect, and our UI itself - currently a single tag - is completely declarative. We can expand on this structure to create a simple form for accepting the input that we need. Once again, the CSS for this project can be found in the book’s repository, but we will not cover styling as part of the lesson.
(defn date-input []
[:div.input-wrapper ;; <1>
[:label "Day"]
[:input {:type "date"}]]) ;; <2>
(defn time-input []
[:div.input-wrapper
[:label "Time (minutes)"]
[:input {:type "number" :min 0 :step 1}]])
(defn submit-button []
[:div.actions
[:button {:type "submit"} "Submit"]])
(defn form []
[:form.input-form
[date-input] ;; <3>
[time-input]
[submit-button]])
(defn app []
[form])
(rdom/render
[app]
(gdom/getElement "app"))
- A class name can be added to an element directly
- HTML attributes can be given as a map following the tag name
- A Reagent component can be provided instead of a tag name
Now that we have a form in place, let’s add a chart above it that will display the data points that the user enters. Since we do not have any real data in state yet, we can just stub out a data structure that has the shape that we want, and we will worry about transforming the actual input into this shape via a reaction later.
(defn- random-point []
(js/Math.floor (* (js/Math.random) 100)))
(defonce chart-data
(let [points (map random-point (range 30))] ;; <1>
(r/atom {:points points
:chart-max (reduce max 1 points)})))
(def chart-width 400)
(def chart-height 200)
(def bar-spacing 2)
(defn chart []
(let [{:keys [points chart-max]} @chart-data ;; <2>
bar-width (- (/ chart-width (count points))
bar-spacing)]
[:svg.chart {:x 0 :y 0
:width chart-width :height chart-height}
(for [[i point] (map-indexed vector points) ;; <3>
:let [x (* i (+ bar-width bar-spacing)) ;; <4>
pct (- 1 (/ point chart-max))
bar-height (- chart-height (* chart-height pct))
y (- chart-height bar-height)]]
[:rect {:key i ;; <5>
:x x :y y
:width bar-width
:height bar-height}])]))
;; ...
;; Change the app function to render the chart too
(defn app []
[:div.app
[chart]
[form]])
- Generate a random number between 0 and 99 for each point
- Dereferencing
chart-datamakes this component reactive (map-indexed vector xs)will produce a sequence of vectors of[idx x]- Calculate the data needed to draw each bar
- Like in React, each item in a sequence should have a unique key
Updating State
Unlike the chat application, which queried the DOM to get the value of its inputs, we are going to invert the responsibility here by putting our input data in state and letting the components render the value from state. Whenever the user makes a change in the input, we want to propagate that change back to state, which will cause our component to re-render. Both React and Reagent refer to this type of input handling as controlled inputs because the value of an input is controlled by UI state. The simplest way to create a controlled input component is to use a slight variation of a Reagent component.
(defn- current-date-string [d]
(let [pad-zero #(.padStart (.toString %) 2 "0")
y (.getFullYear d)
m (-> (.getMonth d) inc pad-zero)
d (pad-zero (.getDate d))]
(str y "-" m "-" d)))
(defonce state
(r/atom {:inputs {:date (date-string (js/Date.))
:minutes "0"}}))
Now we simply need to dereference the state atom within our input components, and they will automatically re-render whenever the state changes.
(defn date-input []
[:div.input-wrapper
[:label "Day"]
[:input {:type "date"
:value (get-in @state [:inputs :date])}]])
If we load the app, it will now populate the date input with today’s date, and it will populate the time input with 0. If you try to update either of these inputs, you will see that they cannot be changed. This is because their value is being set by the UI state, and React will not allow us to update the value of a controlled input. The solution is to add an on-change handler to each of the components that will update the appropriate value within the state with the new value of the input.
(defn date-input []
[:div.input-wrapper
[:label "Day"]
[:input {:type "date"
:value (get-in @state [:inputs :date])
:on-change #(swap! state assoc-in [:inputs :date]
(.. % -target -value))}]])
Components with Setup
Now we can update the inputs. When we change an input, the value in state is updated, which causes the component to re-render (because it dereferences state) with the updated value. Although this works, it is not ideal for performance because every time state changes, Reagent will try to re-render this component. In a larger app, this can cause serious performance problems if every stateful component tries to re-render whenever any piece of state changes. What we want instead is a reaction that only changes when a portion of the app state changes - in this case, only when the appropriate input value changes. Since this is a very common use case, Reagent provides a utility called a cursor. A cursor acts like a reactive atom that points to a specific location inside another reactive atom. When the value at that location is updated, the cursor is updated, and any component that dereferences the cursor is updated. Additionally, the cursor can also be updated with swap! or reset!, and the changes will be reflected in the underlying state.
We could create these cursors as vars at the level of our namespace, but since their use is effectively scoped to a single component, we can create them as a set-up step for our inputs. The components that we just created are the simplest type supported by Reagent - they are functions that evaluate to the DOM (expressed as hiccup) that we want to render. In React terms, these components are simple render functions. However, Reagent allows us to perform some set-up of our component by having our component function return a render function. This will allow us to create a cursor to the input state then return a render function that makes use of this cursor.
(defn date-input []
(let [val (r/cursor state [:inputs :date])] ;; <1>
(fn []
[:div.input-wrapper
[:label "Day"]
[:input {:type "date"
:value @val ;; <2>
:on-change #(reset! val ;; <3>
(.. % -target -value))}]])))
- Create a cursor once before the component is mounted
- Dereference the cursor to make this component reactive
- Update the state via the cursor
When we use a component with setup, the setup step is run only when the component is mounted, whereas the render function that it returns will be called any time the component’s state is updated. The setup step is the rough equivalent of the componentWillMount() lifecycle method in React.
You Try It
We have made several updates to the date-input component: displaying a value from state, updating state, and optimizing rendering using a cursor. Try making the equivalent changes to the time-input component.
Finally, we will deal with form submissions. When the user submits the form, we will set an entry in a data map whose key is the date string and whose value is the number of minutes of exercise done on that day. Upon submission, the form input should also revert to their default state. Let’s go ahead and write a function that makes these changes to state and invoke it as an on-submit handler for the form component.
(defn initial-inputs []
{:date (date-string (js/Date.))
:minutes "0"})
(defonce state
(r/atom {:inputs (initial-inputs)
:entries {}}))
;; ...
(defn submit-form [state]
(let [{:keys [date minutes]} (:inputs state)]
(-> state
(assoc-in [:entries date] (js/parseInt minutes))
(assoc :inputs (initial-inputs)))))
(defn form []
[:form.input-form {:on-submit (fn [e]
(.preventDefault e)
(swap! state submit-form))}
;; ...
])
Now that we have all of the user input handling done, we will next see how to use reactions to write live queries that provide a component with a computed view over the UI state that is automatically kept in sync.
Writing Reactive Queries
So far, the state that we have wanted to render (the input values) has had a one-to-one mapping to the components that we render, but for the chart, we want to re-shape the data before rendering the chart. When we created fake data to use as a stub for the chart, we supplied a sequence of points that should be rendered from left to right as well as a maximum value to determine the height of the y-axis. However, the state contains a map from date to number. We can write a function to generate a sequence of the last 30 days of data, using the user-entered number if available and 0 otherwise. We can then create a reaction that will recalculate the chart data any time the underlying :entries map changes.
(defn get-points [entries]
(let [ms-in-day 86400000
chart-days 30
now (js/Date.now)]
(map (fn [i]
(let [days-ago (- chart-days (inc i))
date (date-string (js/Date. (- now (* ms-in-day days-ago))))]
(get entries date 0)))
(range chart-days))))
(defn chart []
(let [entries (r/cursor state [:entries]) ;; <1>
chart-data (ratom/make-reaction ;; <2>
#(let [points (get-points @entries)]
{:points points
:chart-max (reduce max 1 points)}))]
(fn [] ;; <3>
;; ...
)))
- Get a cursor so that our reaction only re-runs when
:entrieschanges - Create a reaction that re-calculates the chart data whenever :entries changes
- Return the render function that dereferences our
chart-datareaction
Here we update the chart component to use the more advanced form of Reagent component that includes component setup. In the setup, we first get a cursor to the :entries key of the state. This is not strictly necessary, but it allows us to run our reaction only when an entry is changed rather than any time the state is updated. Next, we create a reaction using reagent.ratom/make-reaction. Since the function that we supply dereferences the entries cursor, Reagent re-calculates the value of this reaction whenever the cursor changes. One critical piece to note is that the body of the render function did not change at all. Since the shape of the data that we are querying out of state matches what the component expects, there is no change necessary.
Now the app is fully functional, and if we add an entry using the form, the changes will propagate through the entries cursor, into the chart-data reaction, and finally into the render function of the chart component. We can think of these reactions as live queries into state. We set them up once, and they will provide a flow of data into our components automatically. This data-centric approach that Reagent encourages is a perfect fit with idiomatic ClojureScript.
The Exercise Tracker App
Challenge
This application has no persistence and will be reset if the page is reloaded. Try adding simple persistence using localStorage.
Summary
In this lesson, we learned how to use Reagent for both UI rendering and state management. We saw how Reagent enables declarative components and reactive programming for keeping those components in sync with the application state without any imperative “glue” code. With just a few simple primitives - reactive atoms, cursors, and reactions - we were able to create a stateful application easily and with very few lines of code. We also saw a couple of different types of Reagent components that we can choose between depending on whether a component needs any set-up or not.