Lesson 30: Capstone 5 - Notes
In this section, we have been learning how to use the Reagent framework to apply our ClojureScript knowledge to web applications. In this final capstone lesson, we will once again use a project to synthesize what we have learned about Reagent and modular application design. As in the previous capstone lessons, this one will draw on all that we have learned so far - from working with sequences to state management and asynchronous communication. At this end of this lesson, we will have created a note-taking application from scratch. As was the case in the previous capstone, we will only be building the front-end. In order to follow along, you can use the API running at https://notes.learn-cljs.com/api with a set of credentials that can be obtained by issuing a POST request to https://notes-api.learn-cljs.com/accounts.
In this lesson:
- Create a flexible component-based UI
- Handle state management with Reagent
- Interact with a RESTful API
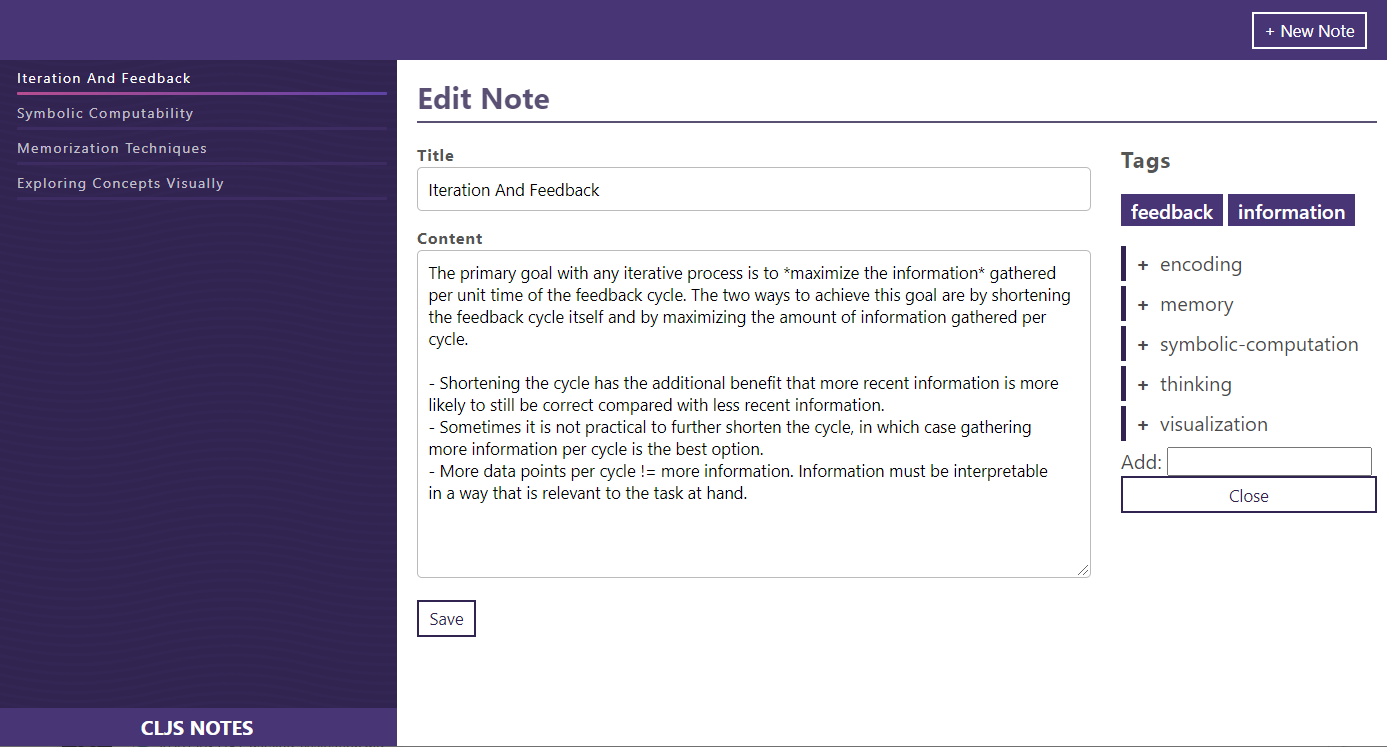
Screenshot of CLJS Notes
What We Are Building
The motivation for this capstone came from the author’s own desire to have a simple note-taking application that could easily be extended as his needs evolved. A user should be able to use this app to take notes, classify them via tags, and edit their collection of notes. The back-end API for this application is deliberately uninteresting for two reasons:
- It is designed to look like most of the APIs that we as web developers interact with at our jobs.
- The primary focus of this lesson is on building UIs, so the less noise introduced by the API, the better.
This app is designed to be used by a single user and does not require any authentication or authorization.
State Management
Now that we know what we are building, it is time to model the data and uncover the patterns that the UI components can use to access that data.
We will start with a basic model for the UI state: notes, tags, and the relationships between them. Since we will be getting the data from a server, we need to consider its data model when deciding how to store and access that data from the UI. We will make use of two primary endpoints: /notes to list all notes, and /tags to list all tags. However - as is the case in most real-world apps - the data will not be in the ideal format for the UI’s consumption, so we will reshape it with a process commonly called normalization.
Data Normalization
One of the main ideas that relational database technology has brought us is the concept of normalization. While normalization does have a technical definition, we can use an informal description: in the canonical application state, data should be shared via references rather than copies. For our purpose, this means that we should store notes and tags separately and maintain a list of the links between them. Additionally, we will structure them in a way that makes lookups efficient. For example, we could receive an API response like the following:
[{:id 1
:title "Books to Read"
:content "..."
:tags [{:id 2 :name "list"}
{:id 3 :name "reading"}]}
{:id 2
:title "Groceries"
:content "..."
:tags [{:id 1 :name "food"}
{:id 2 :name "list"}]}]
The first difficulty with this data structure is that the tags are nested under each note. For note-centric views this is fine, but if we are viewing or editing tags, this structure is less than ideal. We could leave the notes as-is and maintain a separate collection of tags. However, when we edit a tag, we would have to apply the same edit to every copy of that tag that is nested under the notes. The solution here is to do the same thing that we would do if we had a many-to-many relationship in a relational database management system: create separate collections for notes, tags, and the relationships between them. The goal is to transform the data into a shape like the following:
{:notes ;; <1>
{1 {:id 1
:title "Books to Read"
:content "..."}
2 {:id 2
:title "Groceries"
:content "..."}}
:tags
{1 {:id 1 :name "food"}
2 {:id 2 :name "list"}
3 {:id 3 :name "reading"}}}
:notes-tags
{:by-note-id ;; <2>
{1 [2 3]
2 [1 2]}
:by-tag-id
{1 [2]
2 [1 2]
3 [1]}}}
- Each entity is stored in a map indexed by its ID for easy retrieval.
- References are stored in a separate map for each direction (
note -> tagsandtag -> notes) for easy lookup.
You may see that this code does not completely live up to the promise of avoiding duplication. Each reference is effectively stored twice - once for the :by-note-id collection and another time for the :by-tag-id collection. In practice, however, this duplication can be handled in a localized manner so that adding/removing tags from notes is still a simple operation.
To re-shape this data, we need to create several indexes that will enable the following operations to be performed efficiently:
- Look up any note or tag by ID
- Given any note, look up its corresponding tags.
- Given any tag, look up its corresponding notes.
In the case of the tag and note resources, we need a map from ID to resource. Since each ID is unique, there will only be one resource for any given ID. ClojureScript’s group-by function is almost what we want… but not quite:
cljs.user=> (def items [{:id 1 :title "foo"}
{:id 2 :title "bar"}])
#'cljs.user/items
cljs.user=> (group-by :id items)
{1 [{:id 1, :title "foo"}],
2 [{:id 2, :title "bar"}]}
The group-by function takes a group function f and a collection xs, and it returns a map of (f x) to a vector of all items that yielded the same (f x). A keyword is commonly used as the group function so that all items with the same keyword property are grouped together. Since we know that each IDs will have a single element in its group, we can take the first element from every value. The ClojureScript library does not come with a function for transforming every value in a map, but we can write one trivially:
(defn map-values [f m]
(into {} (for [[k v] m] [k (f v)])))
This function uses a for sequence comprehension to iterate over every entry in m, yielding another entry that has the same key but a value that has had f applied. These key, value vectors are then collected into a new map. We can now use this to write a new indexing function:
cljs.user=> (defn make-index [f coll]
(->> coll
(group-by f)
(map-values first)))
#'cljs.user/make-index
cljs.user=> (let [items [{:id 1 :title "foo"}
{:id 2 :title "bar"}]]
(make-index :id items))
{1 {:id 1, :title "foo"},
2 {:id 2, :title "bar"}}
This function works for the primary note and tag indexes, but we need a slightly different strategy for handling the :notes-tags indexes. First, these are not unique indexes, so each group will contain multiple elements. Additionally, these indexes need only sequences of IDs as their values - not full note or tag maps. Therefore, we need to map over the elements in each group and extract a single property from each one. Consider the following:
cljs.user=> (def links [{:note-id 1 :tag-id 2}
{:note-id 1 :tag-id 3}
{:note-id 2 :tag-id 1}
{:note-id 2 :tag-id 2}])
#'cljs.user/links
cljs.user=> (group-by :note-id links)
{1 [{:note-id 1, :tag-id 2} {:note-id 1, :tag-id 3}],
2 [{:note-id 2, :tag-id 1} {:note-id 2, :tag-id 2}]}
Once again, group-by gives us almost what we want. Instead of applying a function to each group (as we did above), we need to apply a function to each item within the group. This is slightly more complicated, but it still requires only the familiar sequence functions that we are used to working with:
cljs.user=> (->> links
(group-by :note-id)
(map-values #(mapv :tag-id %))) ;; <1>
{1 [2 3],
2 [1 2]}
- For each group, map the
:tag-idfunction over every element, yielding a vector.
We can modify the make-index function so that it handles both of the cases that we need by allowing it to take optional functions for transforming each group and transforming each element in the group. One way to handle optional arguments is the “kwargs” (keyword args) pattern. A function’s parameter vector can end with an & followed by a map destructuring pattern. The function will then accept zero or more pairs of arguments that are interpreted as keyword/value pairs. We can now write our final make-index function:
(defn make-index [coll & {:keys [index-fn value-fn group-fn]
:or {value-fn identity
group-fn identity}}]
(->> coll
(group-by index-fn)
(map-values #(group-fn (mapv value-fn %)))))
;; Example usage:
cljs.user=> (make-index items
:index-fn :id
:group-fn first)
{1 {:id 1, :title "foo"},
2 {:id 2, :title "bar"}}
cljs.user=> (make-index links
:index-fn :note-id
:value-fn :tag-id)
{1 [2 3],
2 [1 2]}
With this function written, we need only to write a function to extract all :note-id/:tag-id pairs and a final response normalization function.
(defn get-links [notes]
(mapcat (fn [note]
(for [tag (:tags note)]
{:note-id (:id note)
:tag-id (:id tag)}))
notes))
(defn normalize-notes [notes]
(let [links (get-links notes)
notes-without-tags (mapv #(dissoc % :tags) notes)
all-note-tags (mapcat :tags notes)]
{:notes (make-index notes-without-tags
:index-fn :id
:group-fn first)
:tags (make-index all-note-tags
:index-fn :id
:group-fn first)
:notes-tags
{:by-note-id
(make-index links
:index-fn :note-id
:value-fn :tag-id)
:by-tag-id
(make-index links
:index-fn :tag-id
:value-fn :note-id)}}))
Now that the data normalization is working as we expect, it is time to move on to the architecture that we will use for state management and coordination.
Quick Review
- What is the benefit of normalizing data?
- What is the kwargs pattern? Are there other ways to pass optional parameters to a function?
- Given the normalized data format, how could you reconstruct a note with its tags nested under it?
UI State
In addition to the data that we retrieve from the server, there are a few more pieces of state that we will maintain:
(ns learn-cljs.notes.state
(:require [reagent.core :as r]))
(def initial-state
{:current-route [:home] ;; <1>
:notifications {:messages [] ;; <2>
:next-id 0}
:data {:notes {}
:tags {}}})
(defonce app (r/atom initial-state))
notes/state.cljs
- Route parameters for the current route. The state will serve as the source of truth for routing, and we will be using a routing library to keep the URL in sync with the state.
- Notifications for display using a component adapted from Lesson 29.
This minimal state is all that we need to build the capstone project, so let’s move on to the architecture that we will use to coordinate updates to state.
Coordination Architecture
The architecture that we will use follows the command/event pattern from Lesson 29. The flow will be as follows:
- The UI issues a command by calling a
learn-cljs.notes.command/dispatch!function with a command name and optional payload. - A command handler performs any side effects needed for the command (including calling an API) and may emit events to an event bus.
- State update functions listen for events and update the global application state accordingly.
Another departure from Lesson 29 is that we will not be using core.async for the messaging. While core.async would work here, it is overkill for the simple case where we have one function that emits events and one place where we dispatch to event handlers.
First up is the command dispatcher. This is a simple function that takes a command name and an optional command payload and dispatches to some other function to perform side effects and/or emit events:
(ns learn-cljs.notes.command
(:require [learn-cljs.notes.events :refer [emit!]]))
(defn handle-test-hello! [name]
(println "Hello" name) ;; <1>
(emit! :test/greeting-dispatched {:name name})) ;; <2>
(defn dispatch!
([command] (dispatch! command nil))
([command payload]
(js/setTimeout ;; <3>
#(case command
:test/hello (handle-test-hello! payload)
(js/console.error (str "Error: unhandled command: " command)))
0))
)
notes/command.cljs
- The handler function may perform side effects.
- It should also emit events to which other portions of the app can react.
- Run dispatcher asynchronously so that the call stack can clear before events are handled.
The UI can issue commands by calling _command/dispatch!directly. For example, a component could call(notes.command/dispatch! :test/hello “world”), and the text Hello worldwould be printed to the console. To support more commands, we will add conditions to thecaseexpression indispatch!` and a corresponding handler function.
Next, we need to implement the emit! function that is responsible for delivering events to subscribers. Any code can register a listener function that will be called whenever an event is emitted so that it can have a chance to react to it.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.events)
(def listeners (atom [])) ;; <1>
(defn emit! ;; <2>
([type] (emit! type nil))
([type payload]
(doseq [listen-fn @listeners]
(listen-fn type payload))))
(defn register-listener! [listen-fn] ;; <3>
(swap! listeners conj listen-fn))
notes/events.cljs
- Keep track of the functions to notify when an event is emitted.
- Call each listener function in succession with the event type and payload.
- Allow other code to register a listener.
Note that when we declare listeners, we use def rather than defonce. This is intentional and will allow us to re-register listeners every time the app is reloaded. The result is that when we update event handlers, we do not need to perform a full refresh of the app for the change to be effective.
Finally, we will register a listener that is responsible for performing any necessary updates to the app state when an event occurs.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.state
(:require ;; ...
[learn-cljs.notes.events :as events]))
;; ...
(def handlers (atom {}))
(defn register-handler! [event-type handler-fn]
(swap! handlers assoc event-type handler-fn))
(events/register-listener!
(fn [type payload]
(when-let [handler-fn (get @handlers type)]
(swap! app #(handler-fn % payload)))))
notes/state.cljs
Now, from anywhere in the code, we can register an event handler that will update the app state whenever an event occurs. That handler will be passed the state of the database and the event payload; and it is expected to return a (possibly updated) state for the database.
We created the event bus in such a way that many listeners could be registered, but we only register a listener for state updates. Why the extra layer of indirection rather than allowing the command dispatcher update the app state directly? The main reason is to designate one place to tap into if we want to log events, save them in localStorage to send to a server in an automated bug report, or integrate with a third-part component that is not aware of our state structure. Decoupling the act of emitting an event from updating the app state buys us a lot of flexibility in the long run for very little effort up-front.
To recap to flow of our state management:
- A UI component dispatches a command using
command/dispatch!. - The command dispatcher invokes a handler function, which can emit events and may also perform side effects, such as making API calls.
- The event bus emits the event to listeners.
- The state listener handles the event by passing the event and the current state of the database to any handlers registered for that event.
- An event handler will take the event and the current state of the database and will return an updated state.
- The update state will propagate to any components that depend on it, and they will re-render.
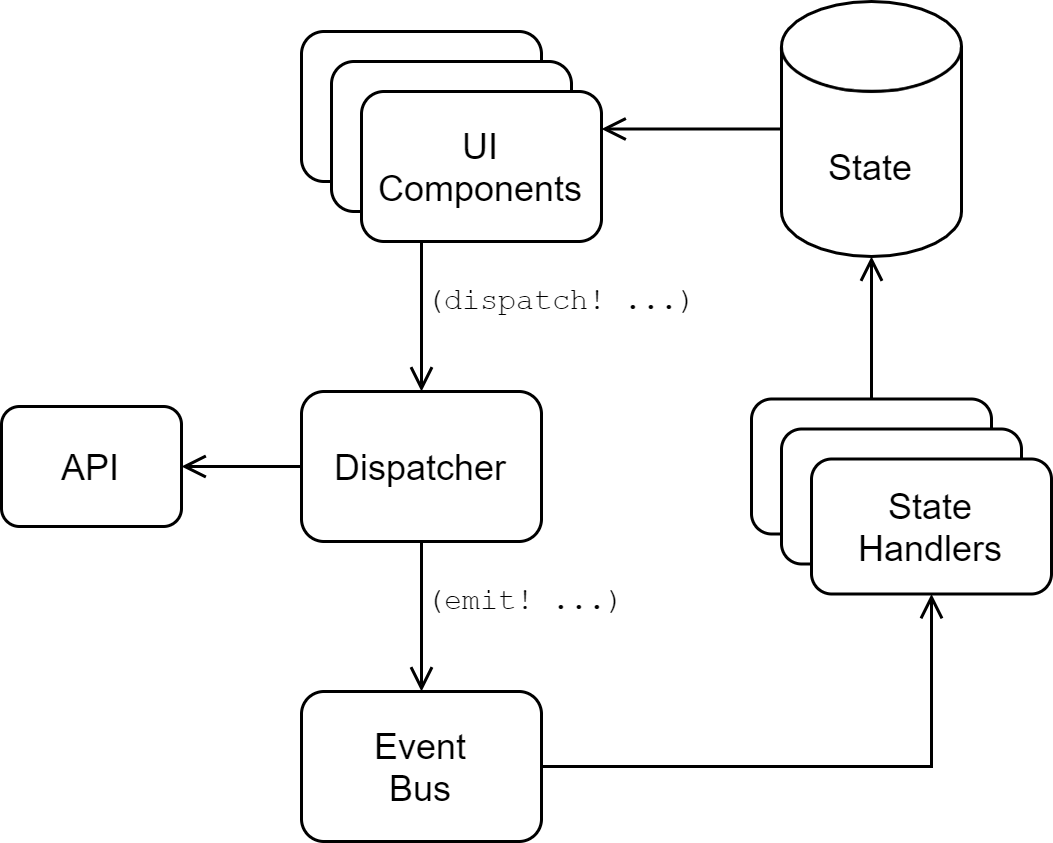
State Coordination
Building the Application
In the first part of this lesson, we focused on a “horizontal slice” of functionality - state management. Since state management is such a core concern to any front-end app, it is important that it is well-designed. However, we will now turn to a “vertical slices” approach to building the rest of the application. That is, we will focus on one feature at a time and develop the UI components, state handlers, API functions, etc. that are related to that feature. After all, that is how most real-world applications are built.
The first “feature” that we will build is the layout. The layout is fairly simple, with a header containing a “New Note” button, a sidebar with a list of notes, and a main content area where the user will create and edit notes.

Layout Shell
We will add most of this structure in our top-level notes.cljs file:
(ns learn-cljs.notes
(:require [learn-cljs.notes.ui.header :refer [header]]
[learn-cljs.notes.ui.main :refer [main]]
[learn-cljs.notes.ui.sidebar :refer [sidebar]]
[learn-cljs.notes.ui.footer :refer [footer]]
[reagent.dom :as rdom]
[goog.dom :as gdom]))
(defn app []
[:div.app
[header]
[main]
[sidebar]
[footer]])
(rdom/render
[app]
(gdom/getElement "app"))
notes.cljs
We have not created the header, main, sidebar, or footer components yet, so let’s do that now, starting with the header.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.header)
(defn header []
[:header.page-header])
notes/ui/header.cljs
The main file will be a similar skeleton for now:
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.main)
(defn main []
[:div.main])
notes/ui/main.cljs
We will then follow the same pattern for the sidebar:
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.sidebar)
(defn sidebar []
[:nav.sidebar])
notes/ui/sidebar.cljs
Next, we will create the footer, which will simply display the name of the application. Since the footer is a static layout component, we will not revisit it for the rest of the lesson.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.footer)
(defn footer []
[:footer.footer "CLJS Notes"])
notes/ui/footer.cljs
Now that we have a little structure in place, let’s start by letting the user create a new note. We will add a button to the header that navigates to a view where the user can fill in their note and save it. Although this seems like a small feature, it will involve:
- adding a few UI components, including the concept of a view
- introducing a router for managing navigation
- creating an API namespace that will control communication with the server
First, we will add the “New Note” button to the header. In the header component, we will require a single button component from _ui.common` (which we will create shortly):
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.header
(require [learn-cljs.notes.ui.common :refer [button]]))
(defn header []
[:header.page-header
[button "+ New Note"
{:route-params [:create-note] ;; <1>
:class "inverse"}]])
notes/ui/header.cljs
- The
:route-paramsoption will control the target of the link.
Before we implement the button component, let’s take a brief detour to discuss routing.
Routing
Like most single-page applications, we will use URL routing to determine which view should be displayed. This presents a challenge, since we the state atom - not the URL - to hold the canonical state of our application, including routing information. In order to manage routing state, we will use the bide library to act as a source of events. Whenever the URL of our application changes, we will treat it as a :route/navigated event that contains the route and any parameters (e.g. the note ID for an :edit-note view). This flow allows us to treat the browser itself as a source of events that may update the application’s state, which remains the single source of truth. One consequence of this method of routing is that we need to allow links and buttons to invoke the router, which will in turn update the URL and emit a :route/navigated event. Thankfully, we already have a command dispatcher abstraction, so our components can just dispatch commands, including routing commands.
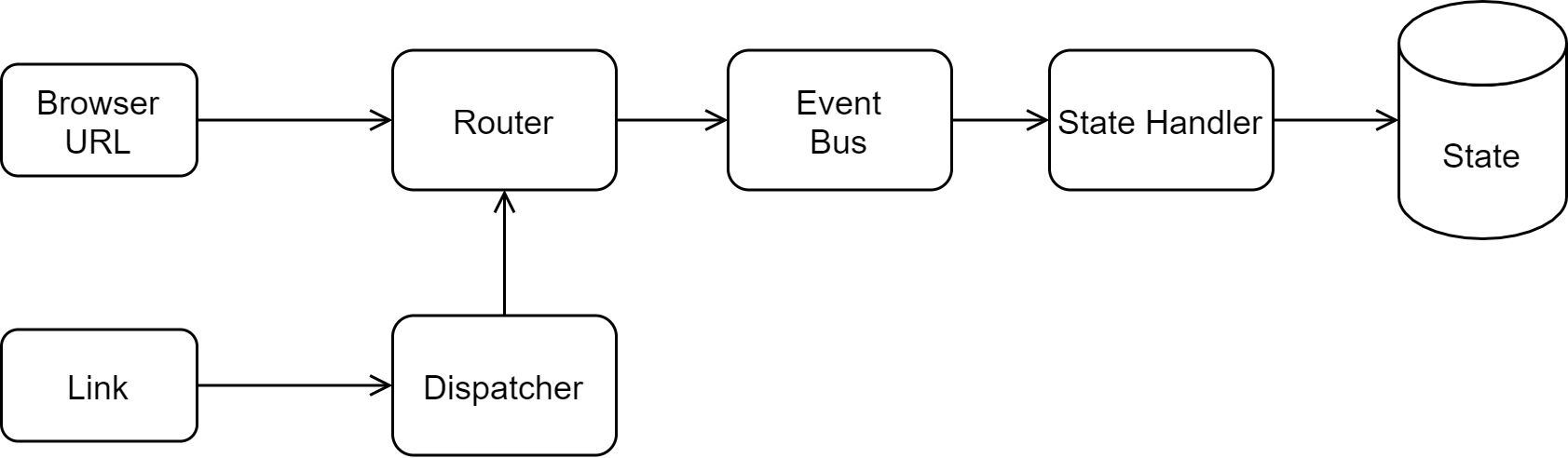
Routing Flow
We will now create a router and hook it up to the relevant pieces of the application. Let’s start by creating a routes namespace that contains the router and related code.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.routes
(:require [learn-cljs.notes.events :refer [emit!]]
[bide.core :as bide]))
(defonce router ;; <1>
(bide/router [["/" :home]
["/notes/new" :create-note]
["/notes/:note-id" :edit-note]]))
(defn navigate! [route-params] ;; <2>
(apply bide/navigate! router route-params))
(defn- on-navigate [name params query] ;; <3>
(emit! :route/navigated [name params query]))
(defn initialize! [] ;; <4>
(bide/start! router {:default :routes/home
:on-navigate on-navigate}))
notes/routes.clj
- Create the router only once
- Side-effecting function that the command dispatcher will call to update the current route
- Callback that will be run whenever the a route change completes
- Initialize the router on startup
Next, we will expose a command in the dispatcher that calls the navigate! function that we just defined:
(ns learn-cljs.notes.command
(:require ;; ...
[learn-cljs.notes.routes :as routes]))
(defn handle-navigate! [route-params]
(routes/navigate! route-params))
;; ...
(defn dispatch
;;...
:route/navigate (handle-navigate! payload))
notes/command.cljs
Now that we have exposed the router to our UI via the dispatcher, let’s initialize the router when the application starts up.
(ns learn-cljs.notes
(:require ;; ...
[learn-cljs.notes.routes :as routes]))
;; ...
(defonce initialized?
(do
(routes/initialize!)
true))
notes.cljs
The reason that we expose an _routes/initialize! rather than initialize the router immediately when _routes is evaluated is that the router will call the on-navigate callback as soon as it is initialized; and if that happens before the event handlers are registered, the state will not be updated. By deferring loading until our core file and all of its imports have been evaluated, we ensure that the initial route event will be handled appropriately. Next, we will create and register the handler for the :route/navigated event.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.event-handlers.routes
(:require [learn-cljs.notes.state :refer [register-handler!]]))
(register-handler!
:route/navigated
(fn [db route-params]
(assoc db :current-route route-params)))
notes/event_handlers/routes.cljs
We will need to evaluate this namespace on startup so that the handler is registered, so let’s take care of that in two steps:
- Create a _event-handlers.core` that requires all event handler namespaces for side effects.
- Require the _event-handlers.core
in our top-level _corenamespace.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.event-handlers.core
(:require [learn-cljs.notes.event-handlers.routes]))
notes/event_handlers/core.cljs
(ns learn-cljs.notes
(:require ;; ...
[learn-cljs.notes.event-handlers.core]))
;; ...
notes.cljs
With all of the plumbing in place, we will update our main component to load different views depending on what route the user is on.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.main
(:require [learn-cljs.notes.state :as state]
[learn-cljs.notes.ui.views.home :refer [home]]))
(defn not-found [] ;; <1>
[:section.hero
[:h1.title "Page Not Found!"]])
(defn main []
(let [[route params query] (:current-route @state/app)] ;; <2>
[:div.main
(case route
:home [home]
[not-found])]))
notes/ui/main.cljs
- Fall back to a generic
not-foundcomponent if the app is at an unknown route - Pull the route parameters out of state to call the appropriate view
As the final step before we return to the feature of creating a new note, we will create the simple home view that we referenced above.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.views.home)
(defn home []
[:div.home.hero
[:h1.title "Welcome to Notes"]
[:h2.subtitle "Select a note or create a new one to get started."]])
notes/ui/views/home.cljs
That was quite an effort to get routing working correctly, but it was worth it! We now have a very clean routing architecture that allows us to easily add views as well as keep our UI components decoupled from the routing mechanism.
Challenge
Update the router to use HTML5 History-based routing instead of hash-based. In order to have this work with the Figwheel dev server, you will need to write a bit of server-side Clojure code.
Creating a New Note
With the length of that detour, I would not blame you if you forgot that we were in the middle of creating a button for adding a new note. Within the ui.header.cljs file, we had added a require for [learn-cljs.notes.ui.common :refer [button]], which we will create now.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.common
(:require [learn-cljs.notes.command :refer [dispatch!]]))
(defn handle-navigate [route-params]
(fn [_]
(dispatch! :route/navigate route-params)))
(defn button [text {:keys [route-params class]
:or {class ""}}]
[:button {:class (str "button " class)
:on-click (handle-navigate route-params)}
text])
notes/ui/common.cljs
For now, our button component acts like a link, which is exactly the behavior that we want. Here is the complete flow of routing that we have just enabled with this button:
- The button will now use the
buttoncomponent to dispatch a:route/navigatecommand with the route params[:create-note]as its payload. - The command dispatcher will pass this command to the router, which will cause the browser’s URL to change.
- The route change will in turn cause the router to emit a
:route/navigatedevent with the new route parameters. - The event handler in
event_handlers/routes.cljswill respond to this event by updating the:current-routeparameter in the application state. - Finally, the
maincomponent will re-render due to the state change and will load a view associated with the:create-noteroute and will render a “Not Found” route as a fallback.
Checkpoint
The app loads with a home page, an empty sidebar, and a button in the header that reads “+ New Note”. Clicking this button navigates to a “Page Not Found” view.
Next, we will create the view for the :create-note route.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.views.note-form
(:require [reagent.core :as r]
[learn-cljs.notes.state :refer [app]]
[learn-cljs.notes.ui.common :refer [button]]))
(defn update-data [data key] ;; <1>
(fn [e]
(swap! data assoc key (.. e -target -value))))
(defn input [data key label] ;; <2>
(let [id (str "field-" (name key))]
[:div.field
[:div.label
[:label {:for id} label]]
[:div.control
[:input {:id id
:type "text"
:on-change (update-data data key)
:value (get @data key "")}]]]))
(defn textarea [data key label]
(let [id (str "field-" (name key))]
[:div.field
[:div.label
[:label {:for id} label]]
[:div.control
[:textarea {:id id
:on-change (update-data data key)
:value (get @data key "")}]]]))
(defn submit-button [data text]
[button text {:dispatch [:notes/create @data]}]) ;; <3>
(defn note-form []
(let [form-data (r/cursor app [:note-form])] ;; <4>
(fn []
[:section.note-form
[:h2.page-title "Edit Note"]
[:form
[input form-data :title "Title"]
[textarea form-data :content "Content"]
[submit-button form-data "Save"]]])))
notes/ui/views/note_form.cljs
- Constructor for an event handler that will set a specific key in the
dataatom - Helper components for the input and textarea
- Re-use the
buttoncomponent used in the header, but with a:dispatchoption - Use a Reagent cursor to select only the state this component needs
Since nothing in this file is particularly novel, let’s return to the button component to add support for a :dispatch option. The intent is that when the button is clicked, it will call the command dispatcher with the command name and payload specified in the value of the option. We can also add an :on-click option that will simply call the provided callback, since we will make use of that option later.
;; ...
(defn handle-dispatch [command-data]
(fn [e]
(.preventDefault e)
(apply dispatch! command-data)))
(defn button [text {:keys [route-params dispatch on-click class]
:or {class ""}}]
[:button
{:class (str "button " class)
:on-click (cond
route-params (handle-navigate route-params)
dispatch (handle-dispatch dispatch)
on-click on-click
:else #(js/console.error "No action provided for button"))}
text])
notes/ui/common.cljs
Now the behavior of the button will vary depending on whether the route-params, dispatch, or on-click option is provided. Remember that cond will evaluate the right-hand side of the first truthy clause in encounters, so the behavior when route-params is specified will not change. However, if dispatch is provided, it will call _command/dispatch!` with the arguments provided.
You Try It
There is quite a bit of duplication between the input and textarea components. Try factoring out the common code into one or more helpers to DRY it up.
The next thing that we need to add is a command handler for :notes/create. This handler will call a function in the API (which we will implement next).
;; ...
(defn handle-create-note! [note]
(api/create-note! note))
(defn dispatch!
;; ...
(case command
;; ...
:notes/create (handle-create-note! payload))
)
Since this is the first bit of server interaction that we are implementing, we could use a couple of utilities - one for performing requests in a consistent manner and one for emitting error notifications that will be displayed in the UI.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.api
(:require [learn-cljs.notes.events :refer [emit!]]
[learn-cljs.notes.errors :as err]
[camel-snake-kebab.core :as csk]
[camel-snake-kebab.extras :as cske]))
(defn do-request!
([method path cb] (do-request! method path nil cb))
([method path body cb]
(let [serialized-body (when body
(->> body ;; <1>
(cske/transform-keys csk/->camelCaseString)
(clj->js)
(js/JSON.stringify)))]
(-> (js/fetch (str js/API_URL path) ;; <2>
(cond-> {:method (name method)
:headers {"Authorization" (str "Bearer " js/API_TOKEN)}
:credentials "include"}
(some? body)
(->
(assoc :body serialized-body)
(update :headers merge {"content-type" "application/json"}))
:always
clj->js))
(.then (fn [res]
(if (.-ok res)
(when (= 200 (.-status res))
(.json res))
(throw (ex-info "API Request Failed"
{:status-code (.-status res)
:status (.-statusText res)}
:api-failure)))))
(.then #(->> %
(js->clj) ;; <3>
(cske/transform-keys csk/->kebab-case-keyword)
(err/ok)
(cb)))
(.catch #(cb (err/error %))))))) ;; <4>
(defn- display-error [err] ;; <5>
(emit! :notification/added
{:type :error
:text (str "API Error: " (ex-message err))}))
(defn create-note! [note] ;; <6>
(do-request! :post "/notes" note
(fn [res]
(->> res
(err/map
#(emit! :note/created %))
(err/unwrap-or display-error)))))
notes/api.cljs
- Convert request body to idiomatic JSON
- Read global variables from the page to determine the API endpoint and credentials
- Convert the response body from JSON to ClojureScript data structures
- Convert any errors that were thrown into error objects
- Helper for emitting error notifications
- At least the code to perform a single request is nice and simple now, right?
There is a lot going on in this file, but the bulk of it is related to the implementation of the do-request! helper. Let’s quickly look at what it is doing. First, it allows client code to specify the HTTP method, URL relative to the API base, an optional body, and a response callback. If a body is supplied, it uses the camel-snake-kebab library to convert Clojure-style snake-case keyword keys to camelCase strings, and it does the inverse to the response body (don’t forget to add camel-snake-kebab/camel-snake-kebab {:mvn/version "0.4.2"} to the project dependencies). It also uses some of the error handling techniques discussed in Lesson 24 to pass either a successful or error result to the callback. The _errors` namespace is taken verbatim from Lesson 24, so it will not be repeated here.
Since we need to read a couple of global variables, let’s open index.html and add these.
<!-- ... -->
<script type="text/javascript">
window.API_URL = "https://notes-api.learn-cljs.com";
window.API_TOKEN =
"Get an API token with: curl -X POST https://notes-api.learn-cljs.com/accounts";
</script>
<!-- ... -->
index.html
The notification component that is used is adapted from Lesson 29 and will not be covered explicitly here. Please see the code in the accompanying repository for reference.
As the final step in creating a new note, we will need to register an event handler for the :note/created event.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.event-handlers.api-data
(:require [learn-cljs.notes.state :refer [register-handler!]]
[learn-cljs.notes.command :refer [dispatch!]]))
(register-handler!
:note/created
(fn [db payload]
(let [{:keys [id title]} payload]
(dispatch! :notification/add
{:type :info
:text (str "Note created: " title)})
(dispatch! :route/navigate ;; <1>
[:edit-note {:note-id id}])
(assoc-in db [:data :notes id] ;; <2>
(dissoc payload :tags)))))
notes/event_handlers/api_data.cljs
- Dispatch a navigation event so that the edit view for this note will load.
- Insert the returned note into the notes index in the application state.
Don’t forget to require this namespace in notes/event_handlers/core.cljs so that it will be evaluated on startup.
Checkpoint
You are able to fill in the title and content on a new note form, and the note is saved to the server when you click the “save” button. You are also redirected to the note edit URL, although there is no view to display yet.
Challenge
This capstone is already massive. You don’t need an extra challenge on this one. Go get yourself a cup of tea!
Listing notes
In comparison to the code that we have added so far, adding a list of notes will be a minor task. For the initial feature of creating a new note, we started from the UI components and worked back to the API. For this feature, let’s do the opposite - focus on how to get the data into the UI, then build the components to display it.
First, we will add a function to the API that calls the “/notes” endpoint to get the full notes list.
;; ...
(defn get-notes! []
(do-request! :get "/notes"
(fn [res]
(->> res
(err/map
#(emit! :notes/received %))
(err/unwrap-or display-error)))))
notes/api.cljs
Yes, 7 lines of code is all we need for this API. The hard work of writing the do-request! helper id paying off. In fact, we can refactor this code a bit more, since the response callback shares a lot of logic with the callback for create-note!. In fact, the only difference is in the function that emits the event. Let’s create another helper function that takes care of the error handling logic.
(defn- with-error-handling [f]
(fn [res]
(->> res
(err/map f)
(err/unwrap-or display-error))))
;; create-note! can also be refactored.
(defn get-notes! []
(do-request! :get "/notes"
(with-error-handling #(emit! :notes/received %))))
Next, we will add a command to the dispatcher that invokes this API function.
;; ...
(defn handle-get-notes! [_]
(api/get-notes!))
;; ...
(defn dispatch
;;...
:notes/get-notes (handle-get-notes! payload))
notes/command.cljs
The next piece is the handler for :notes/received event that the API emits. Although there is quite a bit of work that goes into normalizing the API response, the good news is that we did that work at the beginning of the chapter, and what remains is trivial:
;; ...
;; Paste the final code from the Data Normalization section here
(defn update-normalized-notes [db notes]
(let [{:keys [learn-cljs.notes tags notes-tags]} (normalize-notes notes)]
(update db :data #(-> %
(update :notes merge notes)
(update :tags merge tags)
(assoc :notes-tags notes-tags)))))
(register-handler!
:notes/received
(fn [db payload]
(update-normalized-notes db payload)))
notes/event_handlers/api_data.cljs
Now everything other than the UI is wired up, so let’s open the sidebar file and add a component for listing the notes that came back from the API.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.sidebar
(:require [reagent.core :as r]
[reagent.ratom :as ratom]
[learn-cljs.notes.state :refer [app]]
[learn-cljs.notes.command :refer [dispatch!]]
[learn-cljs.notes.ui.common :refer [link]]))
(defn created-at-sorter [a b] ;; <1>
(> (:created-at a)
(:created-at b)))
(defn notes-list []
(let [notes (r/cursor app [:data :notes])
notes-list (ratom/make-reaction ;; <2>
#(->> @notes
(vals)
(sort created-at-sorter)))]
(dispatch! :notes/get-notes) ;; <3>
(fn []
[:nav
[:ul.notes-list
(for [note @notes-list
:let [{:keys [id title]} note]]
^{:key id}
[:li [link title [:edit-note {:note-id id}]]])]])))
(defn sidebar []
[:nav.sidebar
[notes-list]])
notes/ui/sidebar.cljs
- Function for sorting notes with the newest at the top
- Define the notes list as a reaction over the raw data
- Request notes when the component mounts
For the notes list, we want to display the newest notes first, but our application state only has the notes in a map, where no order is defined. In order to get the sorted list, we can create a reaction that is recomputed only when the underlying notes data changes. Recall the analogy of spreadsheet cells where reactions are like the formulas that connect the cells. The one piece that we are missing is the link component, so let’s add that now.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.common
(:require ;; ...
[learn-cljs.notes.state :as state]
[learn-cljs.notes.routes :as routes]))
;; ...
(defn link [text route-params]
[:a {:href (routes/get-url route-params)
:on-click (handle-navigate route-params)
:class (if (routes/matches? route-params (:current-route @state/app))
"active" "")}
text])
notes/ui/common.cljs
The link component behaves similar to the button, but it also adds an active class when the current route matches the link’s target. This helps us achieve the typical navigation bar functionality where the current link is highlighted. This component relies on two new functions in the _routesnamespace -get-urlandmatches?`, so let’s add them now.
;; ...
(defn get-url [route-params]
(str "#"
(apply bide/resolve router route-params)))
(defn matches? [route-params current-route]
(= (get-url route-params)
(get-url current-route)))
notes/routes.cljs
The get-url function will generate a URL string from route params - exactly the inverse of what happens when we navigate to a new URL and need to infer the route. The matches? function will compare two route parameters to test whether they generate the same URL. This function is used to determine if the browser is currently on some link’s target.
Editing Existing Notes
Since we already have a form for authoring new notes, we now need to generalize it a bit so that it can handle both creating new notes and editing existing ones. The strategy that we will take is to hook into the routing logic to determine whether to set the form data to an empty state or load in some note when the user navigates to the form. Within the form itself, we will make several labels conditional upon whether it is in a creating or editing state, and we will dispatch a different action for create versus update. Since we are re-using the same view, let’s add another entry to the main component’s view switcher.
;;...
(defn main []
;; ...
(case route
:edit-note [note-form]
;; ...
))
notes/ui/main.cljs
Next, let’s add the pieces that we need in the API and command dispatcher. First, the API needs two functions - one to perform the update and another to fetch a single note. The update endpoint does not return the updated note, so we follow up the update with a fetch to ensure that our copy is up to date.
(defn update-note! [note]
(do-request! :put (str "/notes/" (:id note)) note
(with-error-handling
#(emit! :note/updated note))))
(defn get-note! [id]
(do-request! :get (str "/notes/" id)
(with-error-handling #(emit! :note/received %))))
notes/api.cljs
…then the dispatcher:
;; ...
(defn handle-update-note! [note]
(api/update-note! note))
(defn handle-get-note! [id]
(api/get-note! id))
;; ...
(defn dispatch
;;...
:notes/update (handle-update-note! payload)
:notes/get-note (handle-get-note! payload))
notes/command.cljs
Since we want any updates that we make to the note to be reflected in the application state immediately, we need to add an event handler for the :note/updated event. In this handler, we will also dispatch an action to fetch the newly-updated note in its entirety. We will also add the handler to merge this note into our state when the response comes back.
(register-handler!
:note/updated
(fn [db payload]
(let [{:keys [title id]} payload]
(dispatch! :notification/add
{:type :info
:text (str "Note saved: " title)})
(dispatch! :notes/get-note id) ;; <1>
(assoc-in db [:data :notes id] payload))))
(register-handler!
:note/received
(fn [db payload]
(update-normalized-notes db [payload]))) ;; <2>
notes/event_handlers/api_data.cljs
- On update, re-fetch the note
- Re-use the same merging logic that we use for the bulk
:notes/receivedevent
The last piece of state management that we need for this feature is the hook into the routing event handler.
;;...
(defn- note-for-edit-route [db route-params] ;; <1>
(let [note-id (get-in route-params [1 :note-id])
note-id (js/parseInt note-id)]
(get-in db [:data :notes note-id])))
(register-handler!
:route/navigated
(fn [db route-params]
(cond-> db
true (assoc :current-route route-params) ;; <2>
(= :create-note (first route-params)) ;; <3>
(assoc :note-form {})
(= :edit-note (first route-params)) ;; <4>
(assoc :note-form (note-for-edit-route db route-params)))))
notes/event_handlers/routes.cljs
- Given a route to some note’s edit view, return that note from state
- Always update the current route
- When navigating to a create route, clear the form state
- When navigating to an edit route, duplicate the corresponding note as the initial form state
Previously, this handler only updated the :current-route in state, but we just added conditional updates to be performed depending on the route.
Now, let’s go back to the note form and update it so that the appropriate labels are displayed, and dispatch uses the appropriate save action based on whether the user is creating or editing a note. We introduce an is-new? helper that checks the form data for the presence of an ID to determine whether it is a new note.
(defn is-new? [data]
(-> data :id nil?))
(defn submit-button [data] ;; <1>
(let [[action text] (if (is-new? @data)
[:notes/create "Create"]
[:notes/update "Save"])]
[button text {:dispatch [action @data]}]))
(defn note-form []
(let [form-data (r/cursor app [:note-form])]
(fn []
[:section.note-form
[:h2.page-title
(if (is-new? @form-data) "New Note" "Edit Note")]
[:form
[input form-data :title "Title"]
[textarea form-data :content "Content"]
[submit-button form-data]]])))
notes/ui/views/note_form.cljs
- Bind two symbols at once based on some condition
With some relatively minor changes, our app now supports editing notes!
Challenge
Instead of dispatching to either :notes/create and :notes/update, try using a generic :notes/save command that calls a different API endpoint based on whether the note is new.
Tagging Notes
The final feature that we will support in our note-taking app is the ability to apply tags to notes as well as add new tags to the system. There will be three API endpoints that we need to support:
- Listing all tags
- Creating a new tag
- Tagging a note
Let’s go ahead and add commands for each of these actions, followed by the necessary API functions, then the event handlers.
;; ...
(defn handle-get-tags! [_]
(api/get-tags!))
(defn handle-create-tag! [tag-name]
(api/create-tag! tag-name))
(defn handle-tag-note! [{:keys [note-id tag-id]}]
(api/tag-note! note-id tag-id))
;; ...
(defn dispatch
;;...
:tags/get-tags (handle-get-tags! payload)
:tags/create (handle-create-tag! payload)
:notes/tag (handle-tag-note! payload))
notes/command.cljs
Now we’ll move on to the API functions.
(defn get-tags! []
(do-request! :get "/tags"
(with-error-handling #(emit! :tags/received %))))
(defn create-tag! [tag-name]
(do-request! :post "/tags" {:name tag-name}
(with-error-handling #(emit! :tag/created %))))
(defn tag-note! [note-id tag-id]
(do-request! :put (str "/notes/" note-id "/tags/" tag-id)
(with-error-handling
#(emit! :note/tagged {:note-id note-id
:tag-id tag-id}))))
notes/api.cljs
We added three command and three API functions, so it should come as no surprise that we will add three event handlers next.
(register-handler!
:tags/received
(fn [db payload]
(update-in db [:data :tags]
merge (make-index payload
:index-fn :id
:group-fn first))))
(register-handler!
:tag/created
(fn [db payload]
(assoc-in db [:data :tags (:id payload)] payload)))
(register-handler!
:note/tagged
(fn [db payload]
(let [{:keys [note-id tag-id]} payload]
(-> db
(update-in [:data :notes-tags :by-note-id note-id] conj tag-id)
(update-in [:data :notes-tags :by-tag-id tag-id] conj note-id)))))
notes/event_handlers/api_data.cljs
When we receive the list of tags, we use the make-index function that we wrote at the beginning of the lesson to index them by id then merge them on top of any tags that may already be in state. When we create a tag, we simply add it to the indexed tags in state. Finally, when we tag a note, we add entries to both the notes-by-tag and tags-by-notes indexes.
The last piece that we need to add is the UI for managing tags. We will add this as part of the note create/edit form.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.views.note-form
(:require ;; ...
[learn-cljs.notes.ui.tags :refer [tag-selector]]))
;; ...
(defn note-form []
;; ...
[:section.editor
[:form.note ;;...
]
[:div.tags
[:h3 "Tags"]
(if (is-new? @form-data)
[:p.help "Please save your note before adding tags."]
[tag-selector])]]])))
notes/ui/views/note_form.cljs
The main change here is the use of the tag-selector component, which we are about to write. We did restructure some of the DOM here in order to add a level of nesting so that the note form and the tag selector can sit on the page side by side. In order to keep things as simple as possible, we will only support adding tags to notes that have been saved. Otherwise, we would have to keep track of what notes we wanted to add to a new note and add them only once we knew the ID of the note that was created.
Below is the listing for the entire tag-selector component and all of its dependencies. There is a lot going on here, so take you time understanding it. A good portion of the file is dedicated to creating reactions that join data between the tags, indexes, and the note that is being edited.
(ns learn-cljs.notes.ui.tags
(:require [reagent.core :as r]
[reagent.ratom :as ratom]
[learn-cljs.notes.state :refer [app]]
[learn-cljs.notes.ui.common :refer [button]]
[learn-cljs.notes.command :refer [dispatch!]]))
(defn name-sorter [a b]
(< (:name a) (:name b)))
(def all-tags
(r/cursor app [:data :tags]))
(def tags-by-note-index
(r/cursor app [:data :notes-tags :by-note-id]))
(def editing-note-id
(r/cursor app [:note-form :id]))
(def note-tags
(ratom/make-reaction
#(get @tags-by-note-index @editing-note-id)))
(def attached-tags
(ratom/make-reaction
#(->> (select-keys @all-tags @note-tags)
(vals)
(sort name-sorter))))
(def available-tags
(ratom/make-reaction
#(->> (apply dissoc @all-tags @note-tags)
(vals)
(sort name-sorter))))
(defn attached-tag-list []
[:div.attached
(for [tag @attached-tags
:let [{:keys [id name]} tag]]
^{:key id}
[:span.tag name])])
(defn available-tags-list []
[:div
(for [tag @available-tags
:let [{:keys [id name]} tag]]
^{:key id}
[:div.tag {:on-click #(dispatch! :notes/tag {:note-id @editing-note-id
:tag-id id})}
[:span.add "+"] name])])
(defn create-tag-input []
(let [tag-name (r/atom "")]
(fn []
[:div.create-tag
"Add: "
[:input {:value @tag-name
:on-key-up #(when (= (.-key %) "Enter")
(dispatch! :tags/create @tag-name)
(reset! tag-name ""))
:on-change #(reset! tag-name (.. % -target -value))}]])))
(defn available-tag-selector []
(let [is-expanded? (r/atom false)]
(dispatch! :tags/get-tags)
(fn []
[:div.available
(if @is-expanded?
[:div.tag-selector
[available-tags-list]
[create-tag-input]
[button "Close" {:class "block"
:on-click #(reset! is-expanded? false)}]]
[button "+ Add Tags" {:class "block"
:on-click #(reset! is-expanded? true)}])])))
(defn tag-selector []
[:div.tag-selector
[attached-tag-list]
[available-tag-selector]])
notes/ui/tags.cljs
This tag-selector component displays a collection of all of the tags that have been applied to the note that the user is currently viewing. It also contains a drawer with the remaining labels that can be expanded or collapsed, and a label can be applied by clicking on it. Finally, the user can type the name of a new label in the text box and hit Enter to create a new label.
Summary
Now that we have added the last feature to this capstone project, it is time to congratulate yourself. Not only have you completed this capstone, but you have made it through this journey into learning ClojureScript. We started this book with basic lessons on syntax, using somewhat contrived examples to take small steps towards familiarity. We then advanced to projects that synthesized the basic concepts into more useful patterns and constructs. Finally, in this last capstone, we created a well-structured and extensible UI application. This application has an intentional architecture that embraces functional programming, declarative UIs and immutable state management - it is not a toy project.
Thank you, fellow ClojureScript programmer, for joining me on this journey from the basics to real-world programming in this weird and wonderful language. Now go and build some amazing things!